Collision Repair For The Chevrolet Camaro
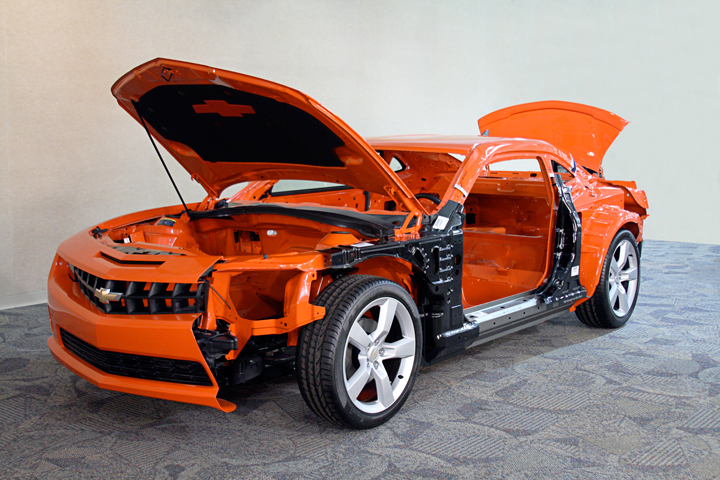

The 2010-2015 Chevrolet Camaro is built on a General Motors global rear-wheel drive platform and shares some of the same chassis parts with the Pontiac GTO and G8. Although the new Camaro looks like a 1969 Camaro, it is quite different from a collision repair point of view. This article covers some of the repair options and considerations when working on a collision-damaged Camaro. General Motors body repair procedures and mechanical/electronic systems can be accessed by visiting www.acdelcotds.com.
Front Lower Rail Sectioning
 Figure 1 - The sectioning location for the inner lower front rail is identified rearward of a reference hole.The front half of a front lower rail may be sectioned using two separate procedures for the inner and outer rails. However, either of these may be done individually if damage is limited to only one side. The cut locations between the inner and outer rails are slightly offset from each other. For the inner rail, the cut location is identified by measuring from a reference hole (see Figure 1). The outer rail is sectioned at the rear edge of the strengthening bead located between the wheelhouse reinforcements.
Figure 1 - The sectioning location for the inner lower front rail is identified rearward of a reference hole.The front half of a front lower rail may be sectioned using two separate procedures for the inner and outer rails. However, either of these may be done individually if damage is limited to only one side. The cut locations between the inner and outer rails are slightly offset from each other. For the inner rail, the cut location is identified by measuring from a reference hole (see Figure 1). The outer rail is sectioned at the rear edge of the strengthening bead located between the wheelhouse reinforcements.
Different joints are used for the inner and outer rails. A butt joint with backing is specified for the inner rail, using a 25 mm sleeve for the backing. The sleeve can be made from an unused portion of the service part. For the outer rail, a flanged lap joint is specified. The service part comes with a pre-stepped portion that fits under the remaining portion of the original rail during installation. Both joints are welded with a combination of GMA plug welds and seam welds. The complete upper rails are available as service parts and replaced at factory seams.
Repair Options for the Rocker Panels
 Figure 2 - The rocker panel reinforcement is made from martensitic ultra-high-strength steel.The outer rocker panels may be sectioned on any of the straight areas on the bottom edge of the door openings. A sectioning joint on the outer rocker panel should be done using a 25 mm overlap joint. The service part is cut to overlap the original outer rocker panel 25 mm. The joint is then seam welded.
Figure 2 - The rocker panel reinforcement is made from martensitic ultra-high-strength steel.The outer rocker panels may be sectioned on any of the straight areas on the bottom edge of the door openings. A sectioning joint on the outer rocker panel should be done using a 25 mm overlap joint. The service part is cut to overlap the original outer rocker panel 25 mm. The joint is then seam welded.
The rocker panel reinforcements are made from ultra-high-strength steel (UHSS) and cannot be straightened or sectioned (see Figure 2). The entire rocker panel reinforcement must be replaced at factory seams if damaged.
Sectioning the Outer A-Pillar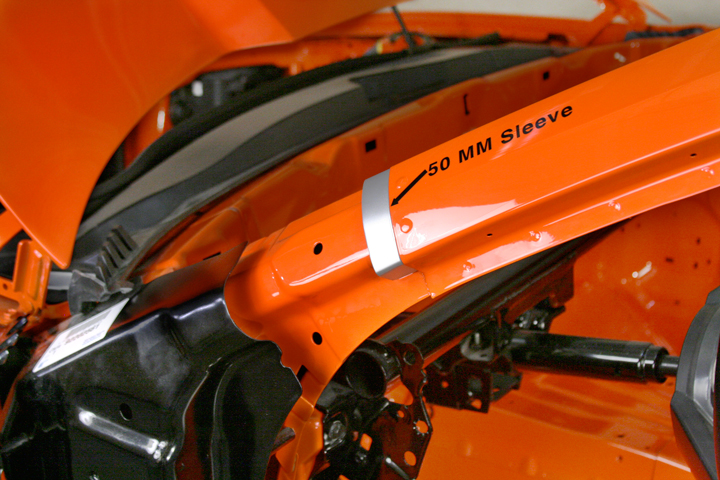 Figure 3 - For the A-pillar, a 50 mm sleeve (backing) may be made from an unused portion of the service part.
Figure 3 - For the A-pillar, a 50 mm sleeve (backing) may be made from an unused portion of the service part.
The lower outer A-pillar may be sectioned on the straight areas of the upper A-pillar and rocker panel. A 50 mm backing is specified for the A-pillar sectioning joint in the windshield area (ee Figure 3). The backing should be trimmed to fit behind the sectioning joint and is attached with plug welds to the vehicle and service part. For the rocker panel sectioning joint, a 100 mm backing plate is specified.
B-Pillar Reinforcement Sectioning
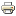
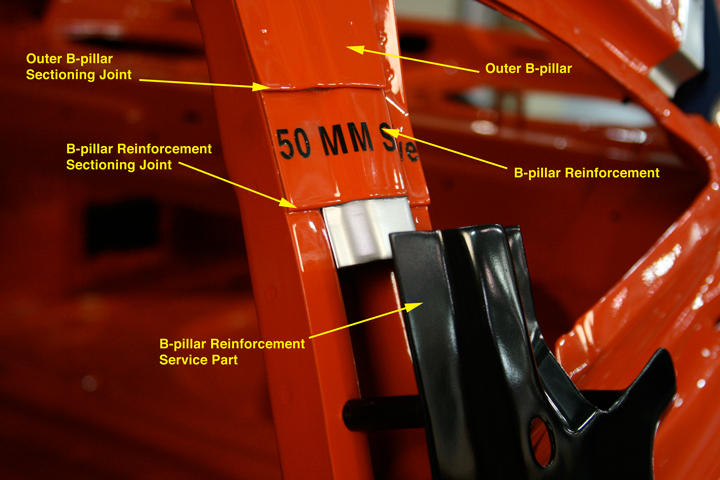 Figure 4 - Various panels and sectioning joints are called out for the B-pillar.The B-pillar reinforcement is made from high-strength, low alloy steel. The sectioning joint should be located 50 mm below the sectioning joint for the outer B-pillar. Refer to the quarter panel sectioning procedure for sectioning the outer B-pillar. A butt joint with backing is used for the B-pillar reinforcement sectioning joint (see Figure 4). The backing can be made from an unused portion of the service part.
Figure 4 - Various panels and sectioning joints are called out for the B-pillar.The B-pillar reinforcement is made from high-strength, low alloy steel. The sectioning joint should be located 50 mm below the sectioning joint for the outer B-pillar. Refer to the quarter panel sectioning procedure for sectioning the outer B-pillar. A butt joint with backing is used for the B-pillar reinforcement sectioning joint (see Figure 4). The backing can be made from an unused portion of the service part.
Quarter Panel Sectioning
The quarter panel may be replaced by sectioning the upper portions of the B- and C-pillars and the rocker panel. The illustrations in the procedure show the general locations for the cuts. The B-pillar reinforcement is used as a backing for the outer B-pillar sectioning joint (see Figure 4). For the upper C-pillar, a 50 mm backing is specified for the sectioning joint. The backing should be made from an unused portion of the replacement part and is attached to the vehicle and service part with GMA plug welds, spaced 40 mm apart. Also note that the foam carrier can be used as a dam for installing replacement foam (see Figure 5). The plastic carrier is available as a replacement part.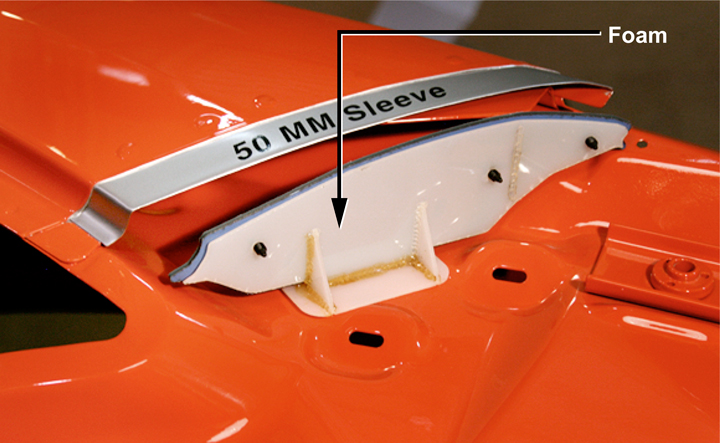 Figure 5 - The foam carrier in the C-pillar is available as a service part.
Figure 5 - The foam carrier in the C-pillar is available as a service part.
General Welding Requirements
General Motors requires the application of weld-through primer to all welding surfaces. Also, use a skip or stitch type of welding method when making seam welds to control heat. It is commonly recommended to trim service parts to allow a 1½ metal thickness root gap for sectioning joints.
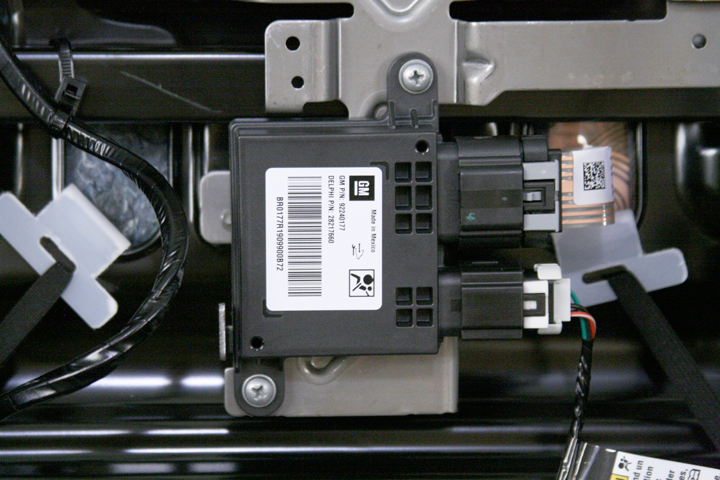 Figure 6 - The control module for the passenger presence system is located under the front passenger seat.
Figure 6 - The control module for the passenger presence system is located under the front passenger seat.
Passenger Presence System (PPS)
The occupant classification system is designed to turn the front passenger airbag OFF if it is not occupied, or occupied by a small child. General Motors refers to this system as the passenger presence system (PPS). The PPS on most GM vehicles requires replacement as an entire calibrated assembly, including the sensor pad, seat cushion foam, and the control module. However, the Camaro has a new type of PPS that allows the control module or seat cushion to be replaced separately (see Figure 6).
The PPS must be rezeroed if any parts of the system have been replaced or the seat cushion trim attachments have been removed. However, the 2010 Camaro is not supported by the Tech 2 scan tool. A multiple diagnostic interface (MDI) unit (see Figure 7) and global diagnostic system (GDS) software is required for rezeroing the PPS on a 2010 Camaro.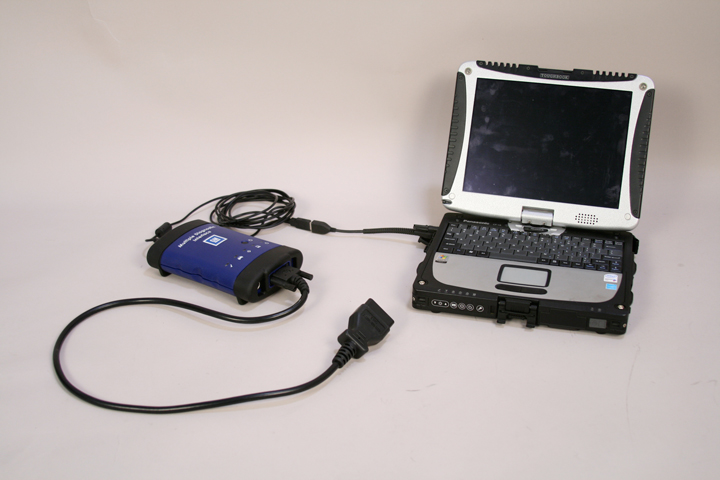 Figure 7 - The multiple diagnostic interface (MDI) connects to a personal computer and is used in conjunction with Global Diagnostic System (GDS) software.
Figure 7 - The multiple diagnostic interface (MDI) connects to a personal computer and is used in conjunction with Global Diagnostic System (GDS) software.
Tire Inflator Kit
No, you probably didn’t misplace the spare tire. A tire inflator and sealer kit (see Figure 8) is standard on all models. However, a conventional spare tire is an option on LS and LT models.
Conclusion
Although the 2010-2015 Chevrolet Camaro has a nostalgic appearance on the outside, the construction and repair methods required are entirely modern. There are several partial replacement procedures that make this car quite repairable in the event of a collision.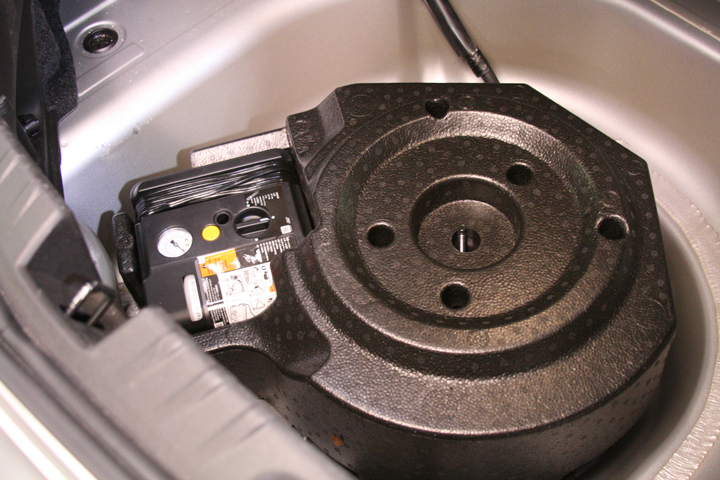  Figure 8 - A tire inflator kit is located in the trunk.
Figure 8 - A tire inflator kit is located in the trunk.
This article first appeared in the December 1, 2009 edition of the I-CAR Advantage Online.
Related I-CAR Courses
Article validated in 2024
-
Toyota/Lexus/Scion Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Thursday, 28 July 2016
As the industry continues to ask if pre- and post-repair system scanning is necessary, Toyota/Lexus/Scion provides their answer.
-
Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning Statements
Wednesday, 9 January 2019
Are you wondering if a particular OEM or organization has a published statement on pre-repair and post-repair scanning? We have compiled a list of most of the statements on the subject, so you can...
-
ADAS, Calibration, And Scanning Article Hotspot
Monday, 14 January 2019
Since advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), scanning, and calibration first started becoming relevant, members of the collision repair industry have required as much knowledge as possible on...
-
Honda/Acura Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning - UPDATE
Wednesday, 22 May 2019
Honda /Acura has updated their position statement on pre- and post-repair scanning to give more clarification on what is expected for scanning.
-
BMW Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning - UPDATE
Friday, 10 April 2020
BMW has released a position statement related to pre- and post-repair system scanning. The statement applies to All vehicles equipped with on board diagnostics II (OBD II).
-
Quickly Identifying Outer Quarter Panels w/Rolled Hem Flanges
Monday, 5 March 2018
The I-CAR best practice article, Recycled Outer Quarter Panels w/Rolled Hem Flanges has gotten a lot of interest from the collision repair industry. It’s important to know which vehicles are...
-
General Motors Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Friday, 21 October 2016
As the industry continues to ask, are pre- and post-repair scans necessary, General Motors provides their answer.
-
Restraints Wiring Repairs
Monday, 23 May 2016
Over the past few months, we've been sharing OEM position statements on restraints wiring repairs. Now we're bringing them all together in one place for easy reference.
-
FCA/Stellantis Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Thursday, 9 June 2016
FCA/Stellantis has released a position statement related to pre- and post-repair system scanning.
-
Typical Calibration Requirements For Forward Radar Sensors
Wednesday, 12 October 2016
Technicians should be aware of what’s required to keep advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) running safely after a collision. Whether that be aiming a camera, which can cause a system to not...
-
I-CAR Repairers Realm: RTS 2025 Year In Review - Now Available
Tuesday, 6 January 2026
I-CAR had a discussion on the Repairability Technical Support (RTS) 2025 year in review.
-
Ford On Target 2025: Volume 4
Monday, 5 January 2026
Ford has released the fourth installment of their On Target publication for 2025.
-
Structural Sectioning Procedures: Ford/Lincoln - UPDATE
Friday, 19 December 2025
Ask I-CAR receives many technical inquiries referring to sectioning. The collision repair industry wants to know where can you section, does the OEM have a sectioning procedure, and where can I find the...
-
Body Repair Manual Symbols: Hyundai
Wednesday, 17 December 2025
While looking at repair procedures in a body repair manual (BRM) you may notice that symbols are used to indicate specific operations or parts to be used during the repair process. Most BRMs provide a...
-
Body Repair Manual Symbols: Genesis
Wednesday, 17 December 2025
While looking at repair procedures in a body repair manual (BRM) you may notice that symbols are used to indicate specific operations or parts to be used during the repair process. Most BRMs provide a...
-
App-Based Connected Services Considerations: BMW
Wednesday, 10 December 2025
Have you had an experience where the vehicle notified the owner that it was being moved while it was in your repair facility? App-based connected services are available from many vehicle makers and...
-
Digital Key Considerations: BMW
Wednesday, 10 December 2025
The intermingling of technology and automobiles continues, with digital key offerings from most vehicle makers. Digital keys utilize smartphone technology to expand vehicle access and owner...
-
Mercedes-Benz Vehicles On The RTS OEM Calibration Requirements Search
Thursday, 4 December 2025
Mercedes-Benz models are now listed in the OEM Calibration Requirements Search page on the RTS website. You're going to notice a difference between other vehicle search results and Mercedes-Benz...
-
I-CAR Repairers Realm - New In 2026: Mixed Attachment Methods And Steel Sectioning Recertification - Now Available
Monday, 1 December 2025
I-CAR had a discussion on the new Mixed Attachment Methods course launching in 2026.
-
Repairer Driven News: SCRS OEM Collision Repair Technology Summit Sessions
Monday, 1 December 2025
Repairer Driven News published three articles highlighting safety inspection topics that took place during the Collision Repair Specialists (SCRS) OEM Collision Repair Technology Summit at the 2025...
- 2026
- January 2026 (2)
- 2025
- December 2025 (8)
- November 2025 (11)
- October 2025 (13)
- September 2025 (11)
- August 2025 (12)
- July 2025 (11)
- June 2025 (11)
- May 2025 (11)
- April 2025 (13)
- March 2025 (12)
- February 2025 (11)
- January 2025 (12)
- 2024
- December 2024 (8)
- November 2024 (10)
- October 2024 (13)
- September 2024 (10)
- August 2024 (12)
- July 2024 (11)
- June 2024 (9)
- May 2024 (13)
- April 2024 (12)
- March 2024 (12)
- February 2024 (12)
- January 2024 (9)
- 2023
- December 2023 (8)
- November 2023 (12)
- October 2023 (11)
- September 2023 (11)
- August 2023 (12)
- July 2023 (9)
- June 2023 (11)
- May 2023 (12)
- April 2023 (11)
- March 2023 (12)
- February 2023 (10)
- January 2023 (11)
- 2022
- December 2022 (11)
- November 2022 (12)
- October 2022 (11)
- September 2022 (13)
- August 2022 (11)
- July 2022 (10)
- June 2022 (13)
- May 2022 (11)
- April 2022 (12)
- March 2022 (10)
- February 2022 (11)
- January 2022 (13)
- 2021
- December 2021 (13)
- November 2021 (11)
- October 2021 (13)
- September 2021 (14)
- August 2021 (12)
- July 2021 (15)
- June 2021 (17)
- May 2021 (11)
- April 2021 (14)
- March 2021 (20)
- February 2021 (14)
- January 2021 (14)
- 2020
- December 2020 (13)
- November 2020 (17)
- October 2020 (12)
- September 2020 (14)
- August 2020 (11)
- July 2020 (18)
- June 2020 (14)
- May 2020 (14)
- April 2020 (19)
- March 2020 (12)
- February 2020 (13)
- January 2020 (14)
- 2019
- December 2019 (13)
- November 2019 (19)
- October 2019 (25)
- September 2019 (20)
- August 2019 (22)
- July 2019 (23)
- June 2019 (20)
- May 2019 (19)
- April 2019 (20)
- March 2019 (20)
- February 2019 (18)
- January 2019 (17)
- 2018
- December 2018 (18)
- November 2018 (19)
- October 2018 (17)
- September 2018 (16)
- August 2018 (21)
- July 2018 (20)
- June 2018 (21)
- May 2018 (17)
- April 2018 (19)
- March 2018 (21)
- February 2018 (15)
- January 2018 (20)
- 2017
- December 2017 (13)
- November 2017 (15)
- October 2017 (19)
- September 2017 (20)
- August 2017 (19)
- July 2017 (18)
- June 2017 (19)
- May 2017 (18)
- April 2017 (13)
- March 2017 (18)
- February 2017 (10)
- January 2017 (11)
- 2016
- December 2016 (9)
- November 2016 (14)
- October 2016 (21)
- September 2016 (10)
- August 2016 (11)
- July 2016 (8)
- June 2016 (10)
- May 2016 (5)
- April 2016 (11)
- March 2016 (12)
- February 2016 (10)
- January 2016 (8)
- 2015
- December 2015 (9)
- November 2015 (6)
- October 2015 (8)
- September 2015 (7)
- August 2015 (11)
- July 2015 (7)
- June 2015 (5)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (8)
- March 2015 (8)
- February 2015 (9)
- January 2015 (10)
- 2014
- December 2014 (12)
- November 2014 (7)
- October 2014 (11)
- September 2014 (10)
- August 2014 (9)
- July 2014 (12)
- June 2014 (9)
- May 2014 (12)
- April 2014 (9)
- March 2014 (6)
- February 2014 (1)
- January 2014 (26)