Nitrogen Hot Air Welding
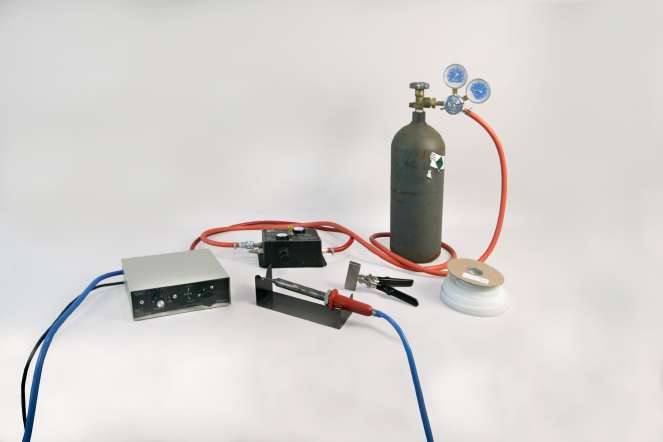 Figure 1 - A nitrogen controller and tank are required to make nitrogen hot air welds.
Figure 1 - A nitrogen controller and tank are required to make nitrogen hot air welds. Hot air welders have been around for a number of years and used mostly in bumper remanufacturing facilities. A hot air welder works by passing compressed air over a heating element and heating the air to around 345°C (650°F) to melt the base plastic and filler rod/ribbon together. This type of welder does not use a flat shoe or feeder tube-type tip. A V-groove is cut into the part, the rod is laid into the V-groove, and the two are melted together. Whenever using this type of welder, it is important to have airflow over the element at all times no matter if it is preheating, welding, or cooling.
A nitrogen hot air welder uses compressed nitrogen gas to eliminate oxygen from the weld area. The nitrogen acts as a shielding gas and allows for a contaminant-free weld with less smoke, which creates a stronger weld (see Figure 1). This type of welder can also switch to compressed air so that when preheating, or cooling down the heating element, it does not waste the nitrogen.
A fusion weld is made when the welding rod and plastic melt and mix together. This type of weld can only be done on thermoplastics. Thermoplastics, such as polypropylene/thermo plastic polyolefin (PP/TPO), which is used to make most bumper covers today, work very well with this type of welder.
Making a Repair
 Figure 2 - Whenever possible, match the ISO code on the part to the filler material.Before any sanding or grinding starts, the part must first be cleaned with soap and water, followed by cleaning with the recommended cleaner. It is also recommended to wipe in one direction to help reduce static. If this step is skipped, the repair may fail due to contamination in the repair area. Once the plastic has been abraded, no solvent cleaners should be used because if any of the solvents become trapped under the repairs it could bubble the repair area in the bake cycle or when it is exposed to the sun.
Figure 2 - Whenever possible, match the ISO code on the part to the filler material.Before any sanding or grinding starts, the part must first be cleaned with soap and water, followed by cleaning with the recommended cleaner. It is also recommended to wipe in one direction to help reduce static. If this step is skipped, the repair may fail due to contamination in the repair area. Once the plastic has been abraded, no solvent cleaners should be used because if any of the solvents become trapped under the repairs it could bubble the repair area in the bake cycle or when it is exposed to the sun.
Identification
When making a nitrogen hot air plastic weld, the need for plastic identification is essential to a successful repair. The plastic identification is primarily used to determine which rod will match the plastic part. It is also helpful to know how the plastic will melt because different plastics will melt at different temperatures. One way to identify the type of plastic is to look at the ISO code that should be located on the backside of the part (see Figure 2). If the ISO code cannot be found, the vehicle maker may have a listing of the types of plastic their parts are made of and may even have a recommended repair procedure.
Once the base material is identified, the technician can select the filler rod to use. Plastic welding rods are usually made of a pure plastic like polypropylene (PP), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) or thermoplastic olefin (TPO). Therefore, they may not match a specific blend of plastic base material. They are available in different diameters and shapes. Some are round rods and others are a flat ribbon. There are also different widths of flat ribbon with the wide ribbons used on the backside as a reinforcement and the more narrow ribbon used as a filler on the front side.
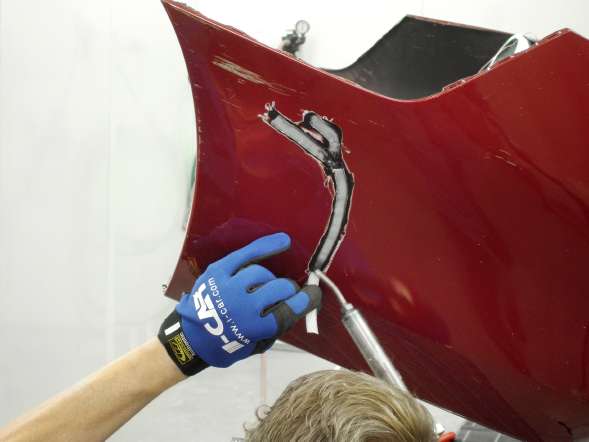 Figure 3 - Protective gloves are recommended in order to prevent burns from the high heat of the nitrogen hot air welder.
Figure 3 - Protective gloves are recommended in order to prevent burns from the high heat of the nitrogen hot air welder.
Repair
After the part has been cleaned and the base material and filler rod have been identified, the part being repaired can be realigned and held in place using aluminum tape. Once the front side is realigned, the backside of the part can be sanded with about P80 grit. Following sanding, the area should be blown clean with clean, oilfree compressed air.
After the nitrogen hot air plastic welder is preheated, the nitrogen gas is turned on and the base material and the welding ribbon are preheated. As the base material and ribbon start to melt, the ribbon is pushed into the base material (see Figure 3). The ribbon will start to fuse to the base material and begin to squeeze out the sides of the ribbon. If a tear goes to an edge of a part, a second smaller ribbon can be laid down across the tear to form a "T" pattern at the edge of the part to add extra strength. Watch the video for a short demonstration of this process (see video).
Once the backside repairs are complete, the aluminum tape can be removed and the tear on the front side can be v-grooved. A v-groove is made on the front side to allow the repair ribbon to be laid down level or slightly lower than the surrounding plastic. Again, make sure that no paint is in the weld area. A smaller ribbon is placed into the v-groove using the same technique as on the backside. Once the weld area has cooled, it should be sanded down and, if necessary, a plastic repair filler should be applied to fill any imperfections.
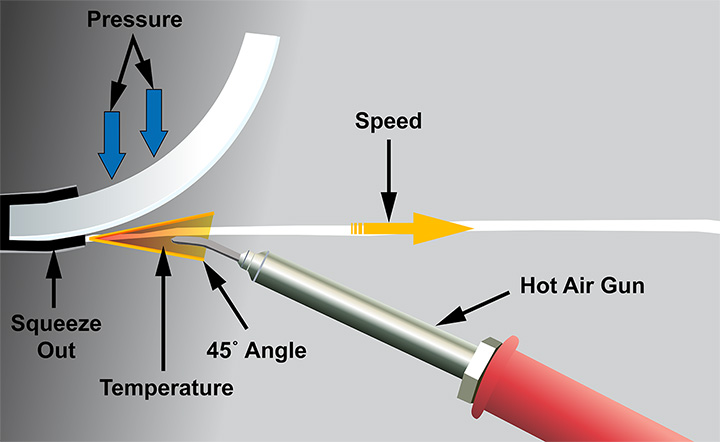 Figure 4 - The technique used to make a nitrogen hot air weld is similar to that of a TIG weld.The acronym TAPS will help the technician remember all the different things to watch while making a nitrogen hot air plastic weld (see Figure 4). The "T" stands for temperature, which must be atthe correct setting to melt the part and the rod. The “A” stands for angle, which should be about 45º to the part. The “P” stands for pressure, which should be firm and constant. The “S” stands for speed, which should allow for 100–150 mm (4"–6") of material to be welded per minute.
Figure 4 - The technique used to make a nitrogen hot air weld is similar to that of a TIG weld.The acronym TAPS will help the technician remember all the different things to watch while making a nitrogen hot air plastic weld (see Figure 4). The "T" stands for temperature, which must be atthe correct setting to melt the part and the rod. The “A” stands for angle, which should be about 45º to the part. The “P” stands for pressure, which should be firm and constant. The “S” stands for speed, which should allow for 100–150 mm (4"–6") of material to be welded per minute.
Precautions
Some welding repair precautions are to never leave any shiny or melted plastic on the part. This will cause poor adhesion of any filler or refinish material. It is also important to featheredge the repair area to make it an invisible repair. With all plastics, never use a solvent on bare plastic. If the vehicle is equipped with an adaptive cruise control or parallel park assist systems, no repair should be done in front of a sensor if it impedes the ability of the sensor to function.
Conclusion
Nitrogen hot air plastic welders are another option to repair plastic parts that otherwise might be discarded. As with any repair technology, it is a business decision to choose to use a repair technology that works best for you.
Related I-CAR Courses
Article validated in 2024
-
Toyota/Lexus/Scion Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Thursday, 28 July 2016
As the industry continues to ask if pre- and post-repair system scanning is necessary, Toyota/Lexus/Scion provides their answer.
-
Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning Statements
Wednesday, 9 January 2019
Are you wondering if a particular OEM or organization has a published statement on pre-repair and post-repair scanning? We have compiled a list of most of the statements on the subject, so you can...
-
ADAS, Calibration, And Scanning Article Hotspot
Monday, 14 January 2019
Since advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), scanning, and calibration first started becoming relevant, members of the collision repair industry have required as much knowledge as possible on...
-
Honda/Acura Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning - UPDATE
Wednesday, 22 May 2019
Honda /Acura has updated their position statement on pre- and post-repair scanning to give more clarification on what is expected for scanning.
-
BMW Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning - UPDATE
Friday, 10 April 2020
BMW has released a position statement related to pre- and post-repair system scanning. The statement applies to All vehicles equipped with on board diagnostics II (OBD II).
-
Quickly Identifying Outer Quarter Panels w/Rolled Hem Flanges
Monday, 5 March 2018
The I-CAR best practice article, Recycled Outer Quarter Panels w/Rolled Hem Flanges has gotten a lot of interest from the collision repair industry. It’s important to know which vehicles are...
-
General Motors Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Friday, 21 October 2016
As the industry continues to ask, are pre- and post-repair scans necessary, General Motors provides their answer.
-
Restraints Wiring Repairs
Monday, 23 May 2016
Over the past few months, we've been sharing OEM position statements on restraints wiring repairs. Now we're bringing them all together in one place for easy reference.
-
FCA/Stellantis Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Thursday, 9 June 2016
FCA/Stellantis has released a position statement related to pre- and post-repair system scanning.
-
Typical Calibration Requirements For Forward Radar Sensors
Wednesday, 12 October 2016
Technicians should be aware of what’s required to keep advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) running safely after a collision. Whether that be aiming a camera, which can cause a system to not...
-
Structural Sectioning Procedures: Ford/Lincoln - UPDATE
Friday, 19 December 2025
Ask I-CAR receives many technical inquiries referring to sectioning. The collision repair industry wants to know where can you section, does the OEM have a sectioning procedure, and where can I find the...
-
Body Repair Manual Symbols: Hyundai
Wednesday, 17 December 2025
While looking at repair procedures in a body repair manual (BRM) you may notice that symbols are used to indicate specific operations or parts to be used during the repair process. Most BRMs provide a...
-
Body Repair Manual Symbols: Genesis
Wednesday, 17 December 2025
While looking at repair procedures in a body repair manual (BRM) you may notice that symbols are used to indicate specific operations or parts to be used during the repair process. Most BRMs provide a...
-
App-Based Connected Services Considerations: BMW
Wednesday, 10 December 2025
Have you had an experience where the vehicle notified the owner that it was being moved while it was in your repair facility? App-based connected services are available from many vehicle makers and...
-
Digital Key Considerations: BMW
Wednesday, 10 December 2025
The intermingling of technology and automobiles continues, with digital key offerings from most vehicle makers. Digital keys utilize smartphone technology to expand vehicle access and owner...
-
I-CAR Repairers Realm: RTS 2025 Year In Review - Coming Soon
Tuesday, 9 December 2025
I-CAR is having a discussion on the Repairability Technical Support (RTS) 2025 year in review.
-
Mercedes-Benz Vehicles On The RTS OEM Calibration Requirements Search
Thursday, 4 December 2025
Mercedes-Benz models are now listed in the OEM Calibration Requirements Search page on the RTS website. You're going to notice a difference between other vehicle search results and Mercedes-Benz...
-
I-CAR Repairers Realm - New In 2026: Mixed Attachment Methods And Steel Sectioning Recertification - Now Available
Monday, 1 December 2025
I-CAR had a discussion on the new Mixed Attachment Methods course launching in 2026.
-
Repairer Driven News: SCRS OEM Collision Repair Technology Summit Sessions
Monday, 1 December 2025
Repairer Driven News published three articles highlighting safety inspection topics that took place during the Collision Repair Specialists (SCRS) OEM Collision Repair Technology Summit at the 2025...
-
I-CAR Audi Collision Repair And Electromechanical Repair Overview Courses
Tuesday, 25 November 2025
I-CAR has developed courses that provide an overview of collision repair and electromechanical repair for current Audi vehicles.
- 2025
- December 2025 (9)
- November 2025 (11)
- October 2025 (13)
- September 2025 (11)
- August 2025 (12)
- July 2025 (11)
- June 2025 (11)
- May 2025 (11)
- April 2025 (13)
- March 2025 (12)
- February 2025 (11)
- January 2025 (12)
- 2024
- December 2024 (8)
- November 2024 (10)
- October 2024 (13)
- September 2024 (10)
- August 2024 (12)
- July 2024 (11)
- June 2024 (9)
- May 2024 (13)
- April 2024 (12)
- March 2024 (12)
- February 2024 (12)
- January 2024 (9)
- 2023
- December 2023 (8)
- November 2023 (12)
- October 2023 (11)
- September 2023 (11)
- August 2023 (12)
- July 2023 (9)
- June 2023 (11)
- May 2023 (12)
- April 2023 (11)
- March 2023 (12)
- February 2023 (10)
- January 2023 (11)
- 2022
- December 2022 (11)
- November 2022 (12)
- October 2022 (11)
- September 2022 (13)
- August 2022 (11)
- July 2022 (10)
- June 2022 (13)
- May 2022 (11)
- April 2022 (12)
- March 2022 (10)
- February 2022 (11)
- January 2022 (13)
- 2021
- December 2021 (13)
- November 2021 (11)
- October 2021 (13)
- September 2021 (14)
- August 2021 (12)
- July 2021 (15)
- June 2021 (17)
- May 2021 (11)
- April 2021 (14)
- March 2021 (20)
- February 2021 (14)
- January 2021 (14)
- 2020
- December 2020 (13)
- November 2020 (17)
- October 2020 (12)
- September 2020 (14)
- August 2020 (11)
- July 2020 (18)
- June 2020 (14)
- May 2020 (14)
- April 2020 (19)
- March 2020 (12)
- February 2020 (13)
- January 2020 (14)
- 2019
- December 2019 (13)
- November 2019 (19)
- October 2019 (25)
- September 2019 (20)
- August 2019 (22)
- July 2019 (23)
- June 2019 (20)
- May 2019 (19)
- April 2019 (20)
- March 2019 (20)
- February 2019 (18)
- January 2019 (17)
- 2018
- December 2018 (18)
- November 2018 (19)
- October 2018 (17)
- September 2018 (16)
- August 2018 (21)
- July 2018 (20)
- June 2018 (21)
- May 2018 (17)
- April 2018 (19)
- March 2018 (21)
- February 2018 (15)
- January 2018 (20)
- 2017
- December 2017 (13)
- November 2017 (15)
- October 2017 (19)
- September 2017 (20)
- August 2017 (19)
- July 2017 (18)
- June 2017 (19)
- May 2017 (18)
- April 2017 (13)
- March 2017 (18)
- February 2017 (10)
- January 2017 (11)
- 2016
- December 2016 (9)
- November 2016 (14)
- October 2016 (21)
- September 2016 (10)
- August 2016 (11)
- July 2016 (8)
- June 2016 (10)
- May 2016 (5)
- April 2016 (11)
- March 2016 (12)
- February 2016 (10)
- January 2016 (8)
- 2015
- December 2015 (9)
- November 2015 (6)
- October 2015 (8)
- September 2015 (7)
- August 2015 (11)
- July 2015 (7)
- June 2015 (5)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (8)
- March 2015 (8)
- February 2015 (9)
- January 2015 (10)
- 2014
- December 2014 (12)
- November 2014 (7)
- October 2014 (11)
- September 2014 (10)
- August 2014 (9)
- July 2014 (12)
- June 2014 (9)
- May 2014 (12)
- April 2014 (9)
- March 2014 (6)
- February 2014 (1)
- January 2014 (26)