Recommended General Motors Steel Repairability Matrix
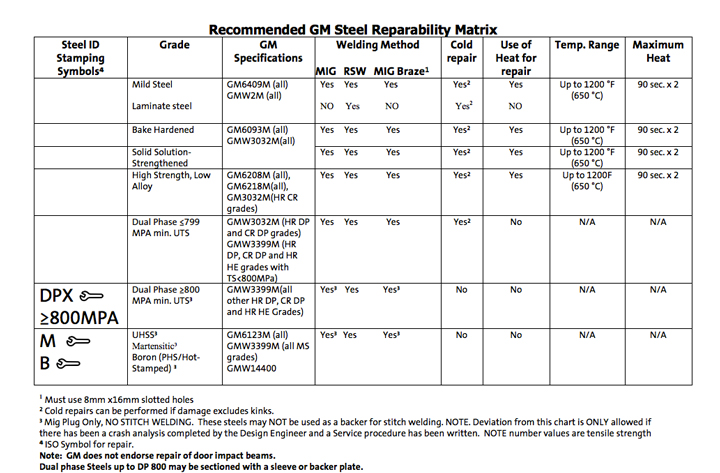
The Recommended GM Steel Repairability Matrix is a chart that identifies GM’s repair recommendations according to the type of steel that the part is made from. The matrix contains information on the steel identification stamping symbols, steel grade, GM specifications, recommended welding methods, cold repairability, use of heat for repairs, the temperature range that should be used, and the maximum heat allotment. The second page of the matrix is a chart of Descriptions of GM Steel.
Matrix Columns
There are eight main columns in this matrix. The first three columns are used to explain the type of steel that is being referenced. The first column identifies the steel ID stamping symbol or International Organization for Standardization (ISO) symbol for the steel. The second column identifies the grade of steel, such as mild, laminated, dual phase, or boron steel. The third column is used by the steel companies to identify the GM specification for the type of steel.
The fourth column identifies whether or not certain types of welding are recommended including GMA welding, squeeze-type resistance spot welding (RSW), and MIG brazing. It is stated in footnote number one that when MIG brazing is recommended, slotted holes 8 x 16 mm should be used. For some steels, like DP>800, UHSS, martensitic, boron, and TRIP, it is noted that GMA plug welds are the only type of GMA welding that is recommended. The footnote stresses that these steels should not be stitch welded during repairs, nor used as a backer for stitch welding. It is noted that “Deviation from this chart is only allowed if there has been a crash analysis completed by the Design Engineer and a service procedure has been written.”
The last four columns address straightening and the use of heat. The fifth column addresses if a steel part may be repaired without the use of heat. If cold repairs are allowed, footnote number two states that it should only be done if the damaged area is not kinked. The sixth column identifies if heat may be used for repairs. When heat is allowed, the last two columns show a maximum temperature of 1200°F (650°C) with heat being applied for no more than 90 seconds and no more than two heat applications.
Additional information in the footnotes includes number three which references sectioning being allowed on DP less than 800 using a sleeve or backer plate. It is also noted that GM does not endorse door impact beam repairs.
Descriptions of GM Steel, found on the second page of the matrix, includes information on the steel grades, alloy content, heat treatment process that are used when making the steel, typical applications of the types of steel, and additional comments.
Conclusion
The Recommended GM Steel Repairability Matrix is a good source for general information on repairing the steels that are found on GM vehicles. Keep in mind that vehicle-specific repair procedures may vary from the general recommendations listed in the matrix based on specific application and design intent. Always reference the repair procedures for the specific vehicle model and year during repairs. The second page of this GM document gives additional information on GM steels including a column that gives typical applications for the types of steel to help make the technician aware of areas where they may encounter these types of steels.
This article first appeared in the September 11, 2007 edition of the I-CAR Advantage Online.
For additional GM information, check out the following pages:
Chevrolet OEM Information
GMC OEM Information
Buick OEM Information
Cadillac OEM Information
Additional I-CAR Collision Repair News you may find helpful:
Related I-CAR Courses
Article validated in 2024
-
Toyota/Lexus/Scion Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Thursday, 28 July 2016
As the industry continues to ask if pre- and post-repair system scanning is necessary, Toyota/Lexus/Scion provides their answer.
-
Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning Statements
Wednesday, 9 January 2019
Are you wondering if a particular OEM or organization has a published statement on pre-repair and post-repair scanning? We have compiled a list of most of the statements on the subject, so you can...
-
ADAS, Calibration, And Scanning Article Hotspot
Monday, 14 January 2019
Since advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), scanning, and calibration first started becoming relevant, members of the collision repair industry have required as much knowledge as possible on...
-
BMW Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning - UPDATE
Friday, 10 April 2020
BMW has released a position statement related to pre- and post-repair system scanning. The statement applies to All vehicles equipped with on board diagnostics II (OBD II).
-
Honda/Acura Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning - UPDATE
Wednesday, 22 May 2019
Honda /Acura has updated their position statement on pre- and post-repair scanning to give more clarification on what is expected for scanning.
-
Quickly Identifying Outer Quarter Panels w/Rolled Hem Flanges
Monday, 5 March 2018
The I-CAR best practice article, Recycled Outer Quarter Panels w/Rolled Hem Flanges has gotten a lot of interest from the collision repair industry. It’s important to know which vehicles are...
-
General Motors Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Friday, 21 October 2016
As the industry continues to ask, are pre- and post-repair scans necessary, General Motors provides their answer.
-
Restraints Wiring Repairs
Monday, 23 May 2016
Over the past few months, we've been sharing OEM position statements on restraints wiring repairs. Now we're bringing them all together in one place for easy reference.
-
FCA/Stellantis Position Statement: Pre- and Post-Repair System Scanning
Thursday, 9 June 2016
FCA/Stellantis has released a position statement related to pre- and post-repair system scanning.
-
Typical Calibration Requirements For Forward Radar Sensors
Wednesday, 12 October 2016
Technicians should be aware of what’s required to keep advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) running safely after a collision. Whether that be aiming a camera, which can cause a system to not...
-
I-CAR Repairers Realm: I-CAR Registered Apprenticeship Program - Coming Soon
Monday, 9 February 2026
I-CAR is having a discussion on the Registered Apprenticeship Program (RAP).
-
SEMA 2025: Lucid Motors Body Repair Team - The New Gravity SUV
Friday, 6 February 2026
I-CAR had numerous presentations at the 2025 SEMA show. One of these presentations focuses on Lucid Motors Gravity SUV repair information.
-
Calibration Research Tips: Blind Spot Indicator In Side Mirrors
Wednesday, 4 February 2026
While searching for information on advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) on an OEM repair information site, you may come across unique calibration procedures or events. These events can vary by...
-
Bumper Cover Repair With ADAS: BMW/Mini - UPDATE
Tuesday, 3 February 2026
A simple bumper repair on a modern vehicle may not be as simple as it seems. New technologies like blind spot monitoring, adaptive cruise control, and other advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)...
-
Hyundai/Genesis Part Replacement Without A Procedure
Thursday, 29 January 2026
We are often asked, “What do I do if there isn’t a procedure to replace a service part?” Let’s see what Hyundai/Genesis says.
-
Kia Part Replacement Without A Procedure
Thursday, 29 January 2026
We are often asked, “What do I do if there isn’t a procedure to replace a service part?” Let’s see what Kia says.
-
I-CAR Repairers Realm: New In 2026: I-CAR Academy - Now Available
Wednesday, 28 January 2026
I-CAR staff had a discussion on the I-CAR Academy.
-
Battery Backup And Low-Voltage Disconnect: Toyota/Lexus
Thursday, 22 January 2026
When an accident happens, how will you call for help? Maybe the telematics system, equipped with a backup battery, could automatically do this, even if the main power is cut off. What are the repair...
-
Your 2025 Favorites: Top 20 Sectioning and Partial Part Vehicles
Wednesday, 21 January 2026
Now that the new year is underway, let’s take a look at your 2025 favorite vehicles in the OEM Partial Part Replacement Search.
-
Your 2025 Favorites: Top Articles
Friday, 16 January 2026
As 2026 rolls in, we can reflect back on what the previous year had to offer. Let's take a look at some of the collision industry information you've been most interested in from this past year....
- 2026
- February 2026 (4)
- January 2026 (11)
- 2025
- December 2025 (8)
- November 2025 (11)
- October 2025 (13)
- September 2025 (11)
- August 2025 (12)
- July 2025 (11)
- June 2025 (11)
- May 2025 (11)
- April 2025 (13)
- March 2025 (12)
- February 2025 (11)
- January 2025 (12)
- 2024
- December 2024 (8)
- November 2024 (10)
- October 2024 (13)
- September 2024 (10)
- August 2024 (12)
- July 2024 (11)
- June 2024 (9)
- May 2024 (13)
- April 2024 (12)
- March 2024 (12)
- February 2024 (12)
- January 2024 (9)
- 2023
- December 2023 (8)
- November 2023 (12)
- October 2023 (11)
- September 2023 (11)
- August 2023 (12)
- July 2023 (9)
- June 2023 (11)
- May 2023 (12)
- April 2023 (11)
- March 2023 (12)
- February 2023 (10)
- January 2023 (11)
- 2022
- December 2022 (11)
- November 2022 (12)
- October 2022 (11)
- September 2022 (13)
- August 2022 (11)
- July 2022 (10)
- June 2022 (13)
- May 2022 (11)
- April 2022 (12)
- March 2022 (10)
- February 2022 (11)
- January 2022 (13)
- 2021
- December 2021 (13)
- November 2021 (11)
- October 2021 (13)
- September 2021 (14)
- August 2021 (12)
- July 2021 (15)
- June 2021 (17)
- May 2021 (11)
- April 2021 (14)
- March 2021 (20)
- February 2021 (14)
- January 2021 (14)
- 2020
- December 2020 (13)
- November 2020 (17)
- October 2020 (12)
- September 2020 (14)
- August 2020 (11)
- July 2020 (18)
- June 2020 (14)
- May 2020 (14)
- April 2020 (19)
- March 2020 (12)
- February 2020 (13)
- January 2020 (14)
- 2019
- December 2019 (13)
- November 2019 (19)
- October 2019 (25)
- September 2019 (20)
- August 2019 (22)
- July 2019 (23)
- June 2019 (20)
- May 2019 (19)
- April 2019 (20)
- March 2019 (20)
- February 2019 (18)
- January 2019 (17)
- 2018
- December 2018 (18)
- November 2018 (19)
- October 2018 (17)
- September 2018 (16)
- August 2018 (21)
- July 2018 (20)
- June 2018 (21)
- May 2018 (16)
- April 2018 (19)
- March 2018 (21)
- February 2018 (15)
- January 2018 (20)
- 2017
- December 2017 (13)
- November 2017 (15)
- October 2017 (19)
- September 2017 (20)
- August 2017 (19)
- July 2017 (18)
- June 2017 (19)
- May 2017 (18)
- April 2017 (13)
- March 2017 (18)
- February 2017 (10)
- January 2017 (11)
- 2016
- December 2016 (9)
- November 2016 (14)
- October 2016 (21)
- September 2016 (10)
- August 2016 (11)
- July 2016 (8)
- June 2016 (10)
- May 2016 (5)
- April 2016 (11)
- March 2016 (12)
- February 2016 (10)
- January 2016 (8)
- 2015
- December 2015 (9)
- November 2015 (6)
- October 2015 (8)
- September 2015 (7)
- August 2015 (11)
- July 2015 (7)
- June 2015 (5)
- May 2015 (7)
- April 2015 (8)
- March 2015 (8)
- February 2015 (9)
- January 2015 (10)
- 2014
- December 2014 (12)
- November 2014 (7)
- October 2014 (11)
- September 2014 (10)
- August 2014 (9)
- July 2014 (12)
- June 2014 (9)
- May 2014 (12)
- April 2014 (9)
- March 2014 (6)
- February 2014 (1)
- January 2014 (26)